Introduction to Machine Learning#
Learning objectives#
Know what Machine Learning and Deep Learning are about.
Understand the main categories of ML systems.
Discover some of the many existing ML algorithms.
Environment setup#
import platform
from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo
print(f"Python version: {platform.python_version()}")
Python version: 3.11.1
Whats is Machine Learning?#
The first definition of Machine Learning#
“The field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.” (Arthur Samuel, 1959).
Machine Learning in a nutshell#
Set of techniques for giving machines the ability to to find patterns and extract rules from data, in order to:
Identify or classify elements.
Detect tendencies.
Make predictions.
As more data is fed into the system, results get better: performance improves with experience.
a.k.a. Statistical Learning.
A new paradigm…#


… Or merely a bag of tricks?#
The Machine Learning landscape#
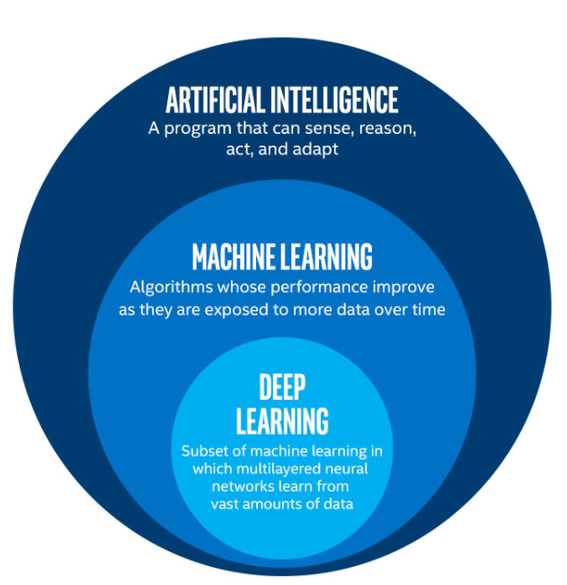
AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning#
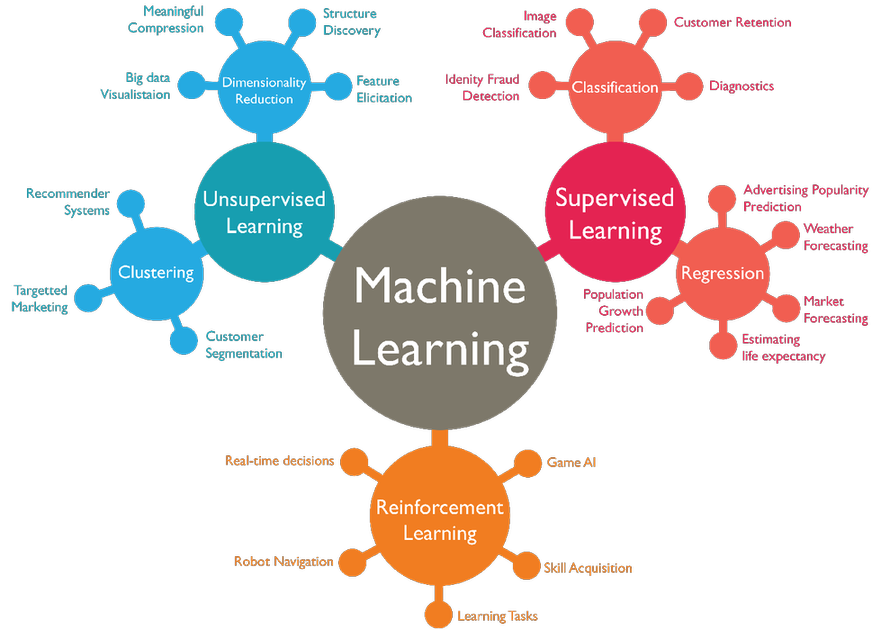
Typology of ML systems#
ML systems are traditionally classified in three categories, according to the amount and type of human supervision during training. Hybrid approaches exist.
Supervised Learning: expected results (called labels or tags) are given to the system along with training data.
Unsupervised Learning: training data comes without the expected results. The system must discover some structure in the data by itself.
Reinforcement Learning: without being given an explicit goal, the system’s decisions produce a reward it tries to maximize.
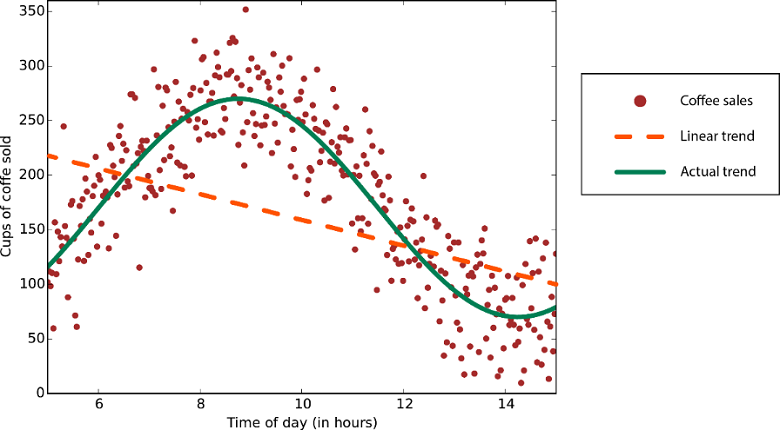
Regression#
The system predicts continuous values. Examples: temperature forecasting, asset price prediction…
Classification#
The system predicts discrete values: input is categorized.
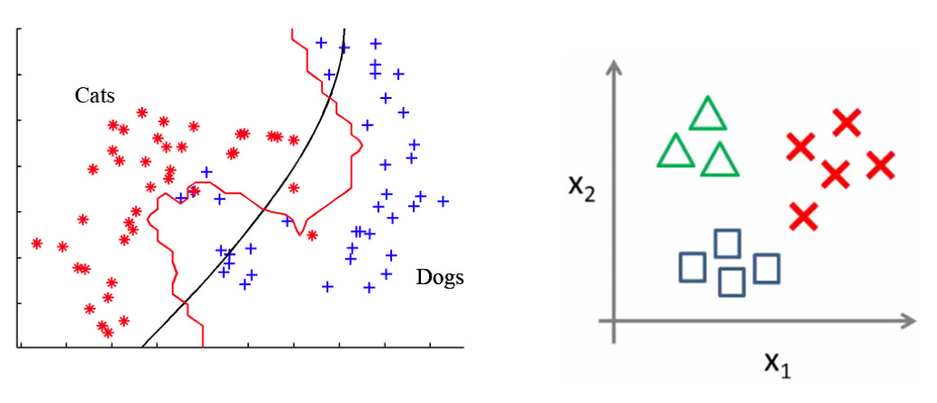
Classification types#
Binary: only two possibles classes. Examples: cat/not a cat, spam/legit mail, benign/malignant tumor.
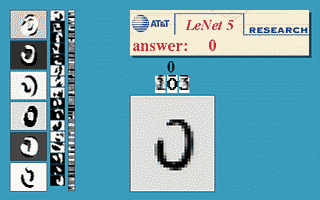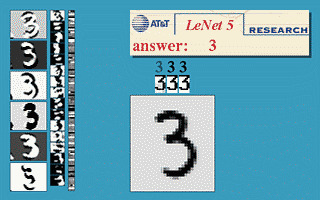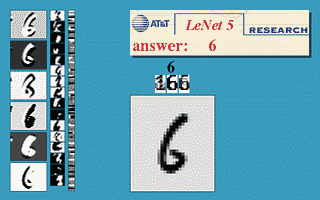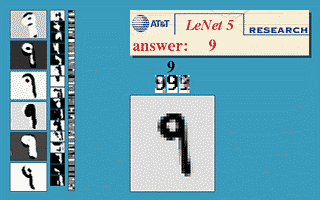
Multiclass: several mutually exclusive classes. Example: handwritten digit recognition.
Multilabel: several non-mutually exclusive classes. Example: face recognition.
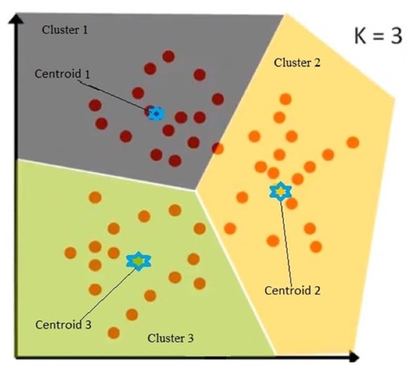
Clustering#
Data is partitioned into groups.
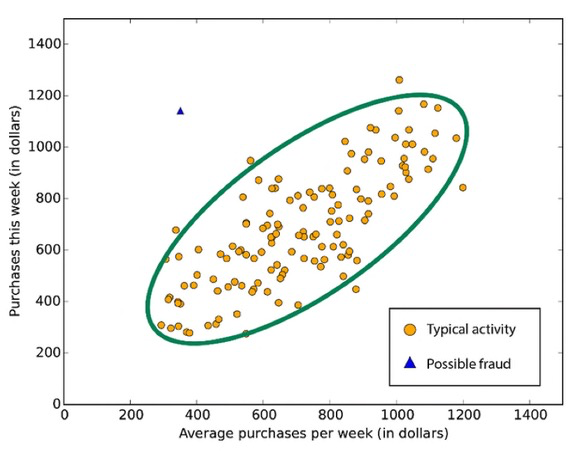
Anomaly Detection#
The system is able to detect abnomal samples (outliers).
Game AI#
Show code cell source
YouTubeVideo("TmPfTpjtdgg")
How do machines learn, actually?#
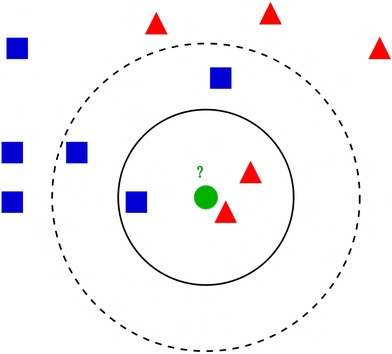
Algorithm #1: K-Nearest Neighbors#
Prediction is based on the k nearest neighbors of a data sample.
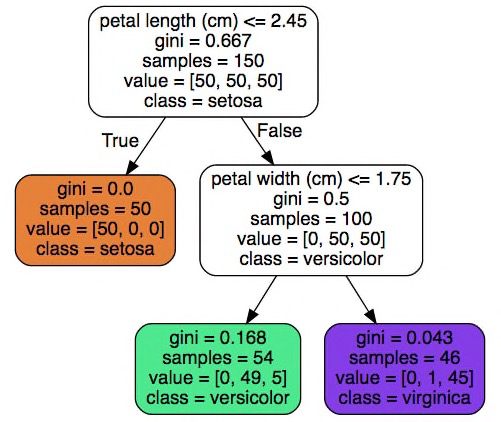
Algorithm #2: Decision Trees#
Build a tree-like structure based on a series of discovered questions on the data.
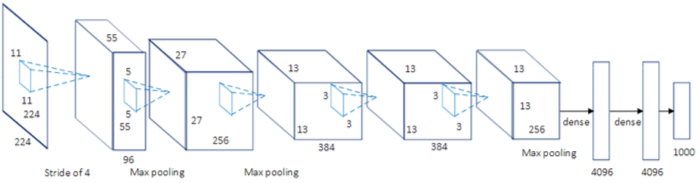
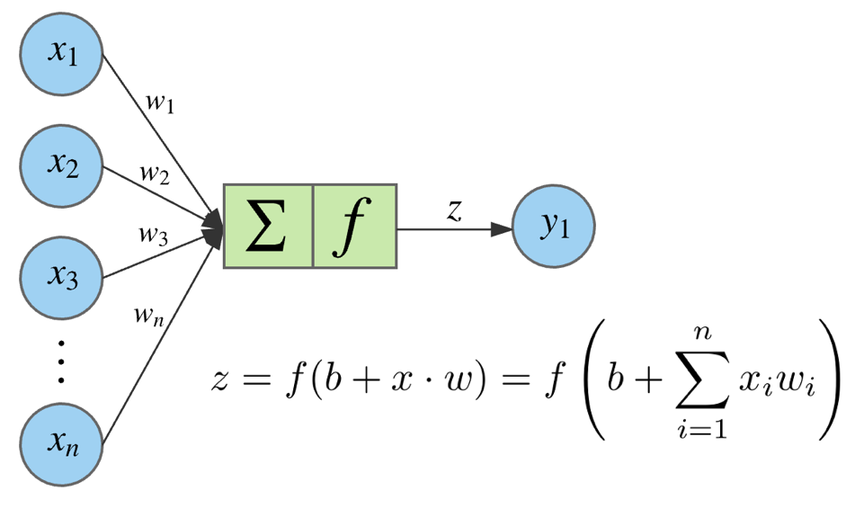
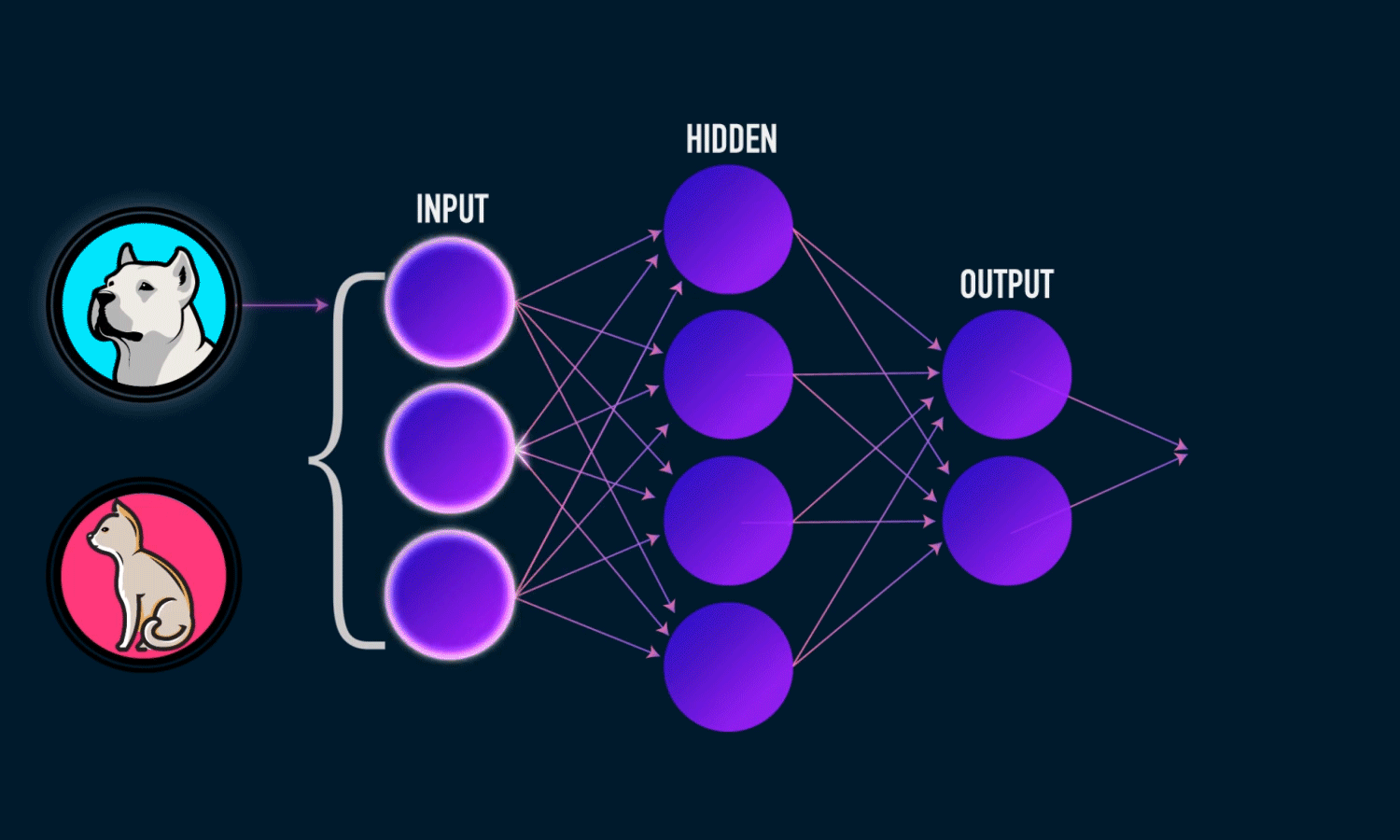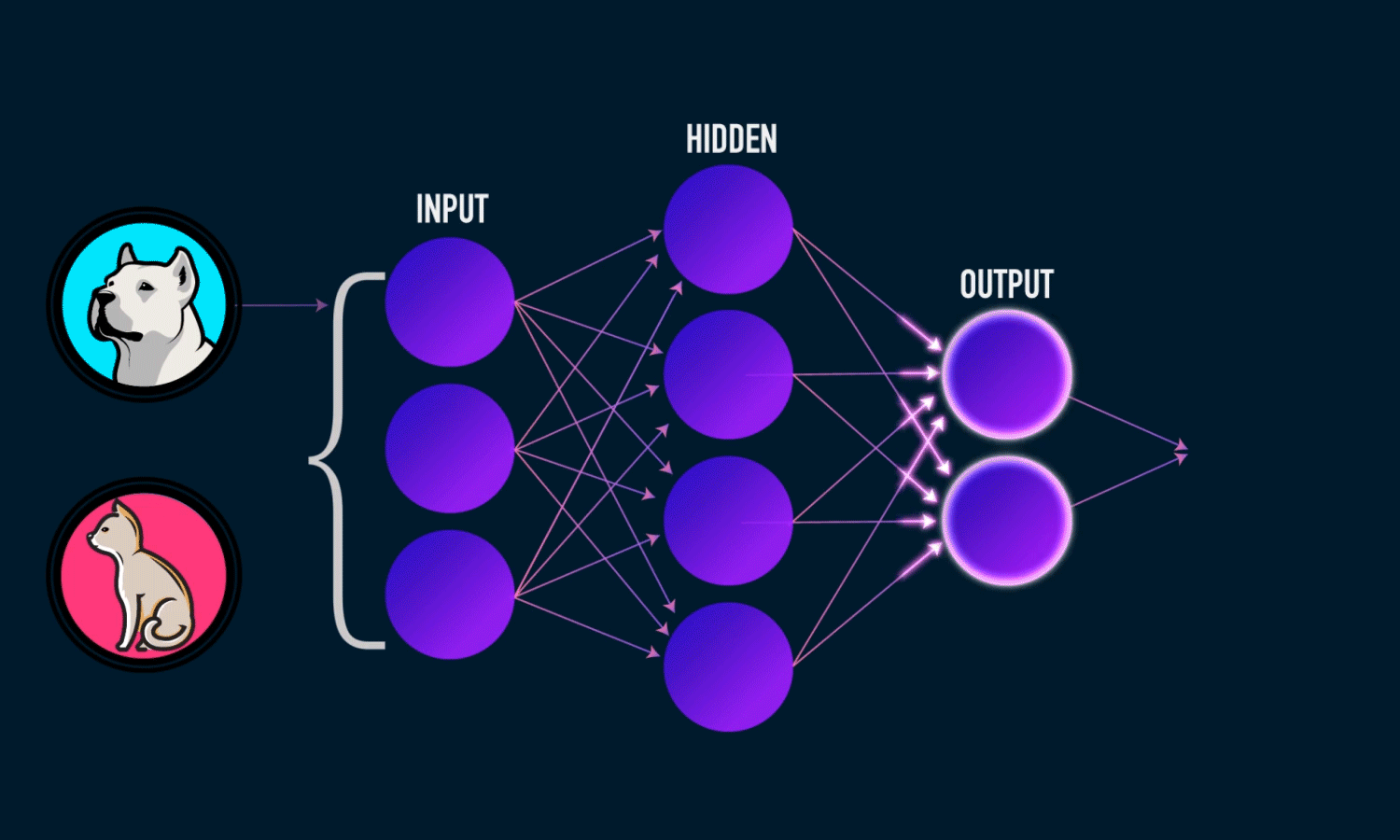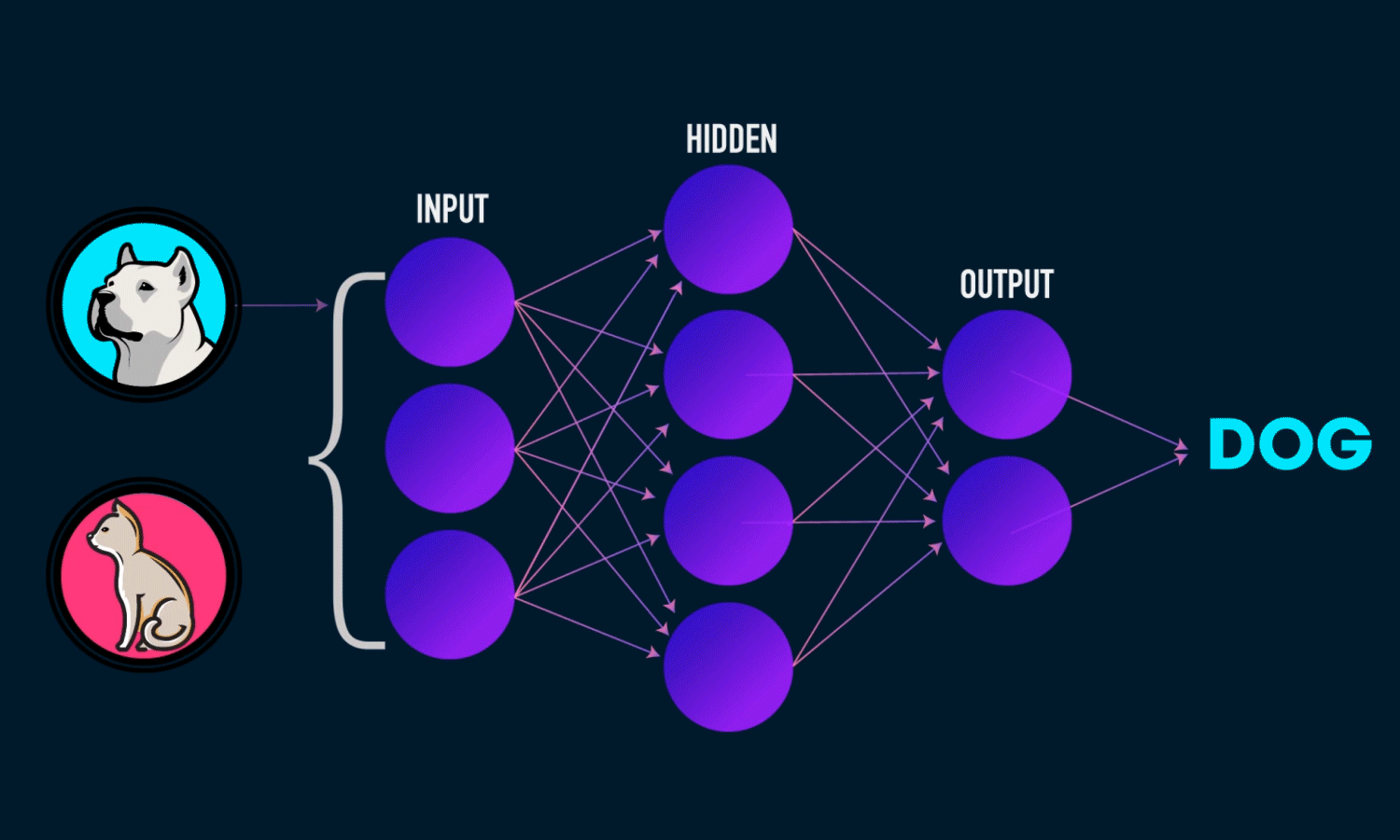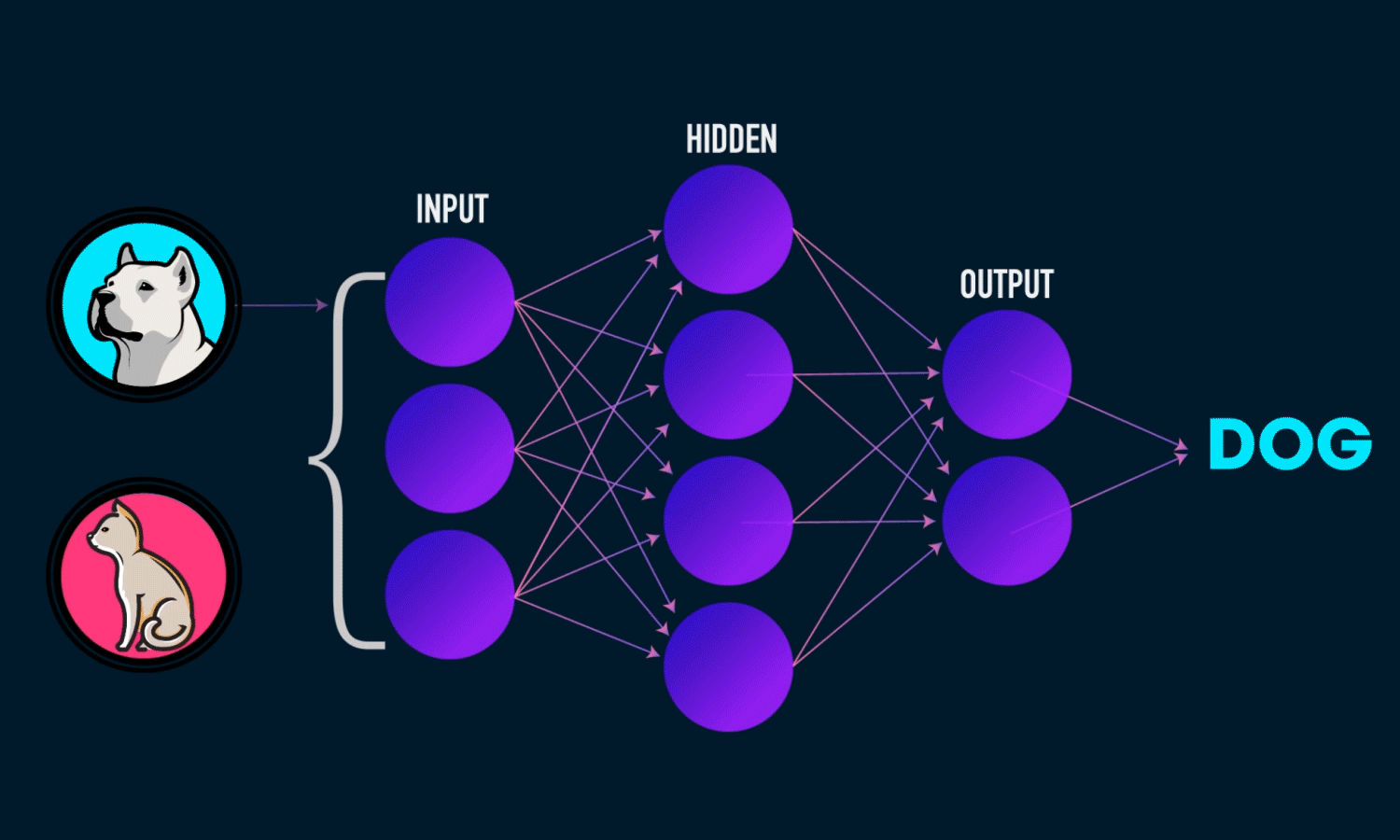
Algorithm #3: Neural Networks#
Layers of loosely neuron-inpired computation units that can approximate any continuous function.
The advent of Deep Learning#
The Deep Learning tsunami#
DL is a subfield of Machine Learning consisting of multilayered neural networks trained on vast amounts of data.
Since 2010, DL-based approaches outperformed previous state-of-the-art techniques in many fields (language translation, image and scene recognition, and much more).
Reasons for success#
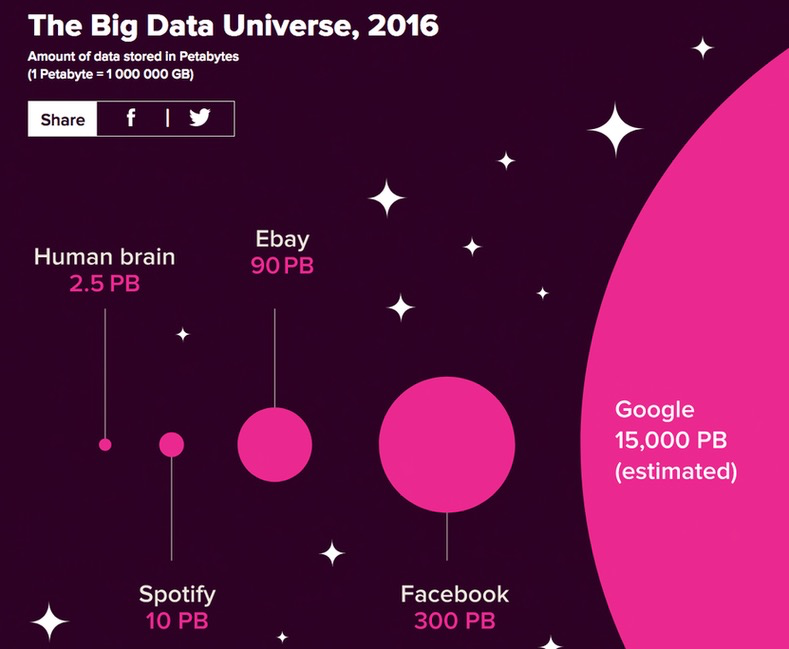
Explosion of available data.
Huge progress in computing power.
Refinement of many existing algorithms.
Availability of sophisticated tools for building ML-powered systems.